"A Look to the Heavens" Barred spiral galaxy NGC 2903
Apr 14, 2017 08:07:13 #
"A Look to the Heavens"
“Barred spiral galaxy NGC 2903 is only some 20 million light-years distant. Popular among amateur astronomers, it shines in the northern spring constellation Leo, near the top of the lion's head. That part of the constellation is sometimes seen as a reversed question mark or sickle. One of the brighter galaxies visible from the northern hemisphere, NGC 2903 is surprisingly missing from Charles Messier's catalog of lustrous celestial sights.
http://4.bp.blogspot.com/-ZQhqIJBsEwM/VeOPSXc9-GI/AAAAAAABdOI/n5yJ-4pPZXA/s1600/N2903JewelofLeo_hallas_c1024.jpg
This colorful image from a small ground-based telescope shows off the galaxy's gorgeous spiral arms traced by young, blue star clusters and pinkish star forming regions. Included are intriguing details of NGC 2903's bright core, a remarkable mix of old and young clusters with immense dust and gas clouds. In fact, NGC 2903 exhibits an exceptional rate of star formation activity near its center, also bright in radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and x-ray bands. Just a little smaller than our own Milky Way, NGC 2903 is about 80,000 light-years across.”
- http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap150410.html
“Barred spiral galaxy NGC 2903 is only some 20 million light-years distant. Popular among amateur astronomers, it shines in the northern spring constellation Leo, near the top of the lion's head. That part of the constellation is sometimes seen as a reversed question mark or sickle. One of the brighter galaxies visible from the northern hemisphere, NGC 2903 is surprisingly missing from Charles Messier's catalog of lustrous celestial sights.
http://4.bp.blogspot.com/-ZQhqIJBsEwM/VeOPSXc9-GI/AAAAAAABdOI/n5yJ-4pPZXA/s1600/N2903JewelofLeo_hallas_c1024.jpg
This colorful image from a small ground-based telescope shows off the galaxy's gorgeous spiral arms traced by young, blue star clusters and pinkish star forming regions. Included are intriguing details of NGC 2903's bright core, a remarkable mix of old and young clusters with immense dust and gas clouds. In fact, NGC 2903 exhibits an exceptional rate of star formation activity near its center, also bright in radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and x-ray bands. Just a little smaller than our own Milky Way, NGC 2903 is about 80,000 light-years across.”
- http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap150410.html
Apr 16, 2017 23:57:24 #
I must tell you how much I enjoy your Heavenly postings. I look at them for a few seconds, and a great calm covers me. Thank you.
Apr 17, 2017 06:28:23 #
pafret wrote:
"A Look to the Heavens" br br br âBa... (show quote)
Super cool!!!!! Seeing things such as this always intrigues me and starts the how old, when formed, why, what's its function if anything?? Etcetcetc..
Check the difference in technology from yours to this one...
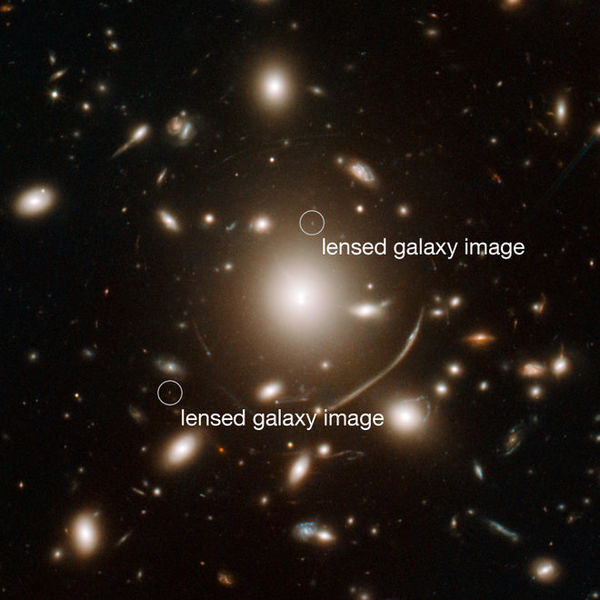
Using the galaxy cluster Abell 383 (center) as a "gravitational lens," astronomers identified a galaxy so far away we see it as it was 950 million years after the Big Bang. It is visible as two tiny dots on either side of Abell 383. Distant objects seen through gravitational lenses are typically multiply imaged and heavily distorted.
Credit: NASA, ESA, J. Richard (CRAL), J.-P. Kneib (LAM). Acknowledgement: Marc Postman (STScI)
The first galaxies may have formed much earlier than thought, a new study suggests â just 200 million years or so after the universe's birth.
Using several different telescopes, astronomers have discovered a distant galaxy whose stars appear to have formed 200 million years after the Big Bang, the explosive event that brought the universe into being.
That's about 300 million years earlier than the oldest previously known galaxies. The universe itself is estimated to be 13.7 billion years old.
The finding could force astronomers to rethink what they seem to know about the cosmos and its early days, researchers said.[Photo of the newfound galaxy]
"This challenges theories of how soon galaxies formed and evolved in the first years of the universe," study lead author Johan Richard, of France's Center of Astronomical Research of Lyon, said in a statement. "It could even help solve the mystery of how the hydrogen fog that filled the early universe was cleared."
How do we know the real age of these things?? I mean st best it's guesstimating.. I seriously question how they know the Universe is 13. 7 billion years old or the big band theory is as they say~~
Well now you've put the brain melt into action and it's just my first cup of coffee.. Thanks


Apr 17, 2017 08:50:43 #
lindajoy wrote:
Super cool!!!!! Seeing things such as this always ... (show quote)
Very interesting Photo Linda. You can clearly see the banana shaped arc of light in the lower right side which is the indicator of the gravity lenses effect on the distant galaxy's light. There is a possible smaller arc on the left lower left quadrant of the massive distorted beach ball, of the galaxy forming the lens. The two dots are the same distant galaxy beyond the lens; the light approaching the gravity lens from the other side got split into two images. Some of these gravity lenses split the image into multiple appearances.
Some mind boggling concepts here, empty space being 'bent' by the effects of "Dark Matter", light peeking around the corners of the shadows. Just 200 million years away from the big bang; I expect to see creation appear on the Discovery channel very soon.
Apr 17, 2017 09:22:39 #
pafret wrote:
Very interesting Photo Linda. You can clearly see... (show quote)
Thank You, pafret for your distinguished explanation of the reflective light.. I can clearly see the banana shaped arch and the beach ball effect...I did note the distance between the two galaxy .. Would that suggest they are closer to us than thought as well?? Isn't that the only way we can truly see them is if close enough ? I remember once reading that, which lead me to wonder about the Scientific conclusion of where the stars, galaxies and plants really are in measurement to light years?? Or to us??
And I ask because the ladder analogy arises because no single technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy??? Correct???
Apr 17, 2017 12:31:48 #
lindajoy wrote:
Thank You, pafret for your distinguished explanati... (show quote)
While it seems like magic or guesswork these distances can be measured with very good accuracy.
This link is to a page which goes into detail:
http://www.sciencemeetsreligion.org/physics/distance.php
Basically it is a combination of trigonometry, parallax (measuring from two distant terrestrial points), measurement of light output and comparison with standard candles and known stars in our own galaxy. It is not one straight forward measurement but the aggregate of a number of factors. It still seems like magic but it works. Read the article at the link for a better understanding; it has some interesting pictures and diagrams which may help.
The fact that the lensing effect occurred says that the "two" galaxies are beyond the massive galaxy causing the distortion in the space field. The two images are really only one galaxy, the light was split as it approached the lens and appeared as two spots
If you want to reply, then register here. Registration is free and your account is created instantly, so you can post right away.

